
6 Day Galapagos Itinerary
Day 1: Arrival & Chinese Hat Islet
Chinese Hat is a small island is located in the central area of Galapagos, just of the south eastern tip of Santiago Island. It is named after its unique cone hat looking shape formed from volcanic activity many years ago. The visit offers rare, up close viewing of Galapagos wildlife and well preserved remnants of fragile volcanic rock that can’t be found in such a unique condition anywhere else. The islet is home to a colony of sea lions on the white coral sand beach.
Day 2: Isabela Island: Vicente Roca Point & Fernandina Island: Espinosa Point
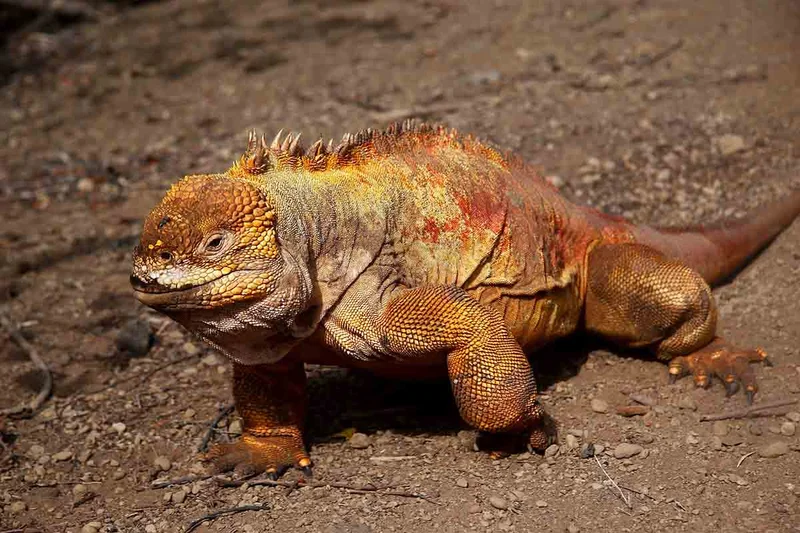
Isabela Island is the largest of all the Galapagos Islands, about 120 km long, and is peculiarly shaped like a sea-horse! It is one of the few islands that are populated. The last census that was taken estimated about 2,200 people living on the Southern part of the Island. The island was formed by 6 different shield volcanoes from North to South that erupted continuously, eventually joining together to form on entire land mass. Of all the islands in the archipelago, Isabela is the most active with the latest eruption coming from Wolf Volcano in May of 2015. There are lots of unique wildlife on Isabela such as the pink iguana, and more wild tortoises than any other island with a different type of species near each of the 6 volcanoes.
On Vicente Roca Point the geological formations are simply outstanding and it is a great place to view various bird species such as blue-footed boobies, Nazca boobies, gulls, storm petrels, and brown noddy terns. Activities here are all done on the water by either dinghy or panga, or snorkeling. On this western part of the island the Cromwell Current provides cold water and many nutrients. Due to this it is possible to see various feeding frenzies of an assortment of animals such as whales, dolphins, sea lions, and marine birds diving. At times it may also be likely to see fur seals.
In Fernandina Island, no foreign species have ever invaded it and therefore it is one of the world’s most pristine island ecosystems. It is one of the most active islands and is the westernmost island in the archipelago. The volcano “La Cumbre” dominates the landscape with lava fields reaching the ocean. The Cromwell Current also flows on the west making the cold and nutrient-rich water an ideal habitat for the Galapagos Penguin and Flightless Cormorant that nests here.
Day 3: Isabela Island: Tagus Cove & Urbina Bay
Tagus Cove is located on the upper west part of the island and was named after and English war ship that used to pass the islands in the 1800’s. This was a famous spot for many pirates and sailors who have even left their names and the names of the ship inscribed on volcanic rock. There are many different characteristics of the island here from various volcanic activities such as large volcanic rocks or small little balls of petrified rain. On the hike the path leads to Darwin Lake with a tuff cone.
A bit more south of Tagus Cove is Urbina Bay. Urbina Bay is an interesting site due to the uplifts of the island caused by volcanic and tectonic activity. When it rose, so did the corals and reefs that were under the surface. You can still see them although they are beginning to deteriorate due to air exposure. There are chances of seeing giant tortoises, land iguanas, and more flightless cormorants near the coast.
Day 4: Isabela Island: Elizabeth Bay & Moreno Point
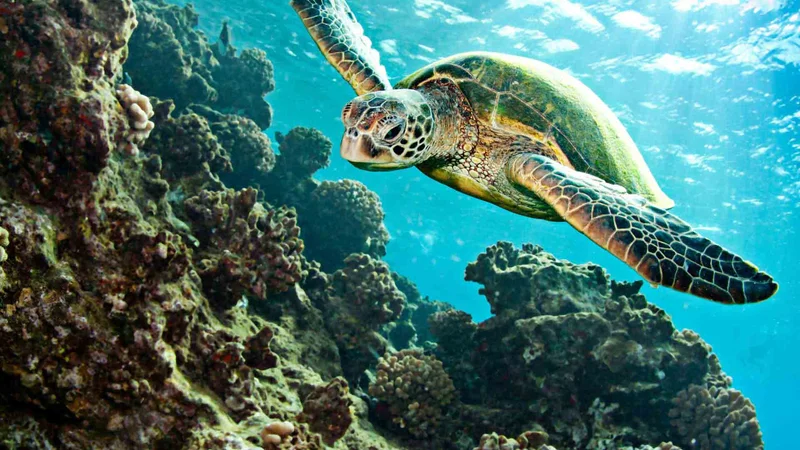
A visitor site on the way down to the southern parts of Isabela Island is Elizabeth Bay. There are a series of islets, a lagoon and mangroves surrounding it. The mangroves provide a great place to observe many birds and at the lagoon, it is possible to see sea turtles resting and feeding.
On the South Western point of Isabela Island is Moreno Point. With striking black geological features, it is home to endemic species known only to the barren lava flows found here. Various activities are possible such as a hike, a panga ride to better see various seabirds, geological features, and snorkeling to view the vibrant underwater life.
Day 5: Santa Cruz Island: Charles Darwin Station & Highlands
Nowadays Santa Cruz is one of the most popular tourist sites. With a population of about 12,000 Galapagos natives, it has the longest paved road in the entire archipelago. One of the biggest conservation efforts is to eliminate all non-native plants and animals that are destroying native and endemic species on the island. There is no longer any volcanic activity but that does not mean there is no evidence. Santa Cruz means holy cross, but it’s English name comes from the British vessel – Indefatigable.
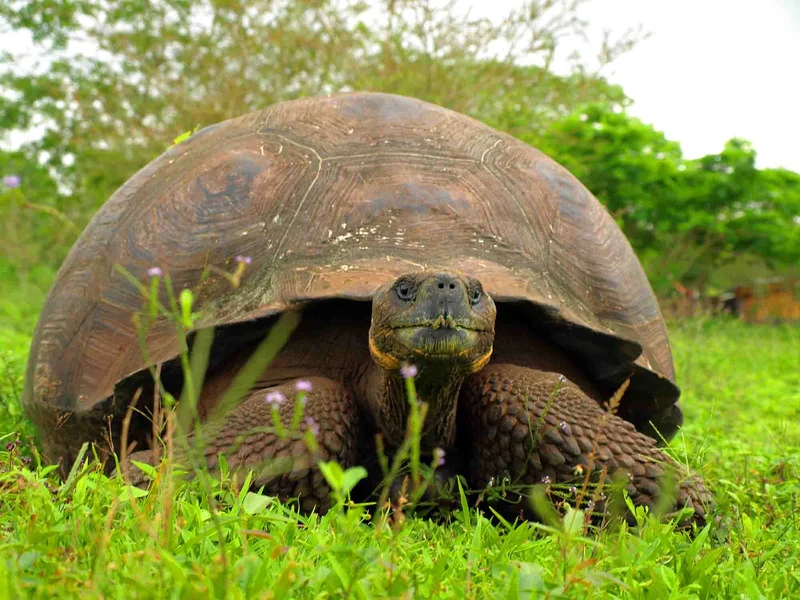
Charles Darwin Research Station conducts many different research projects and provides assistance to other researchers and governmental institutions and agencies, especially the Galapagos National Park. Many of the results are later published online, in magazines, and popular scientific journals. The research station also plays a big part in educating the community and public schools in Galapagos. There is also the longtime running Giant Tortoise restoration program that includes various stages of the giant tortoise from eggs, hatchlings and adults.
In the highlands, you can walk along a path made to observe the hills, ferns, volcanoes, and rich wildlife. This area is home to Giant Tortoises, mockingbirds, Bahama ducklings, White-cheeked Pintails, Darwin finches and many other species. Lava tubes here are more than half a mile long. Walking along these lava tubes is a unique and surreal experience.
Day 6: South Plaza Island & Departure
San Cristobal Island is the fifth largest island in the Galapagos and lies farthest East. It is where Darwin first landed back in 1835 and where the first permanent settlements were founded. Today the main port Puerto Baquerizo Moreno is the capital of the Galapagos province and houses many government offices, the Ecuadorian Navy, and an airport with daily flights to the mainland of Ecuador. Conservation challenges the island faces include invasive plants like blackberry and guayaba and insects like the blackfly.
Lobos Island is an islet about an hour away from San Cristobal. Blue-footed boobies will nest here seasonally. In recent years frigate birds have begun to nest here. Sea lions are abundant, as well as marine iguanas. It is a very calm and tranquil site with beautiful views, including Kicker Rock off in the distance.
La Galapaguera, this Interpretation Center has been open to the public since 1998 and offers extensive information about the history of Galapagos, all ecosystems, geology, and flora and fauna. Giant tortoises are also bred here by the center and roam about in a semi-natural habitat created by the centers’ employees. Within the center are meeting rooms, interpretational panels, auditoriums, exhibits, and much more.
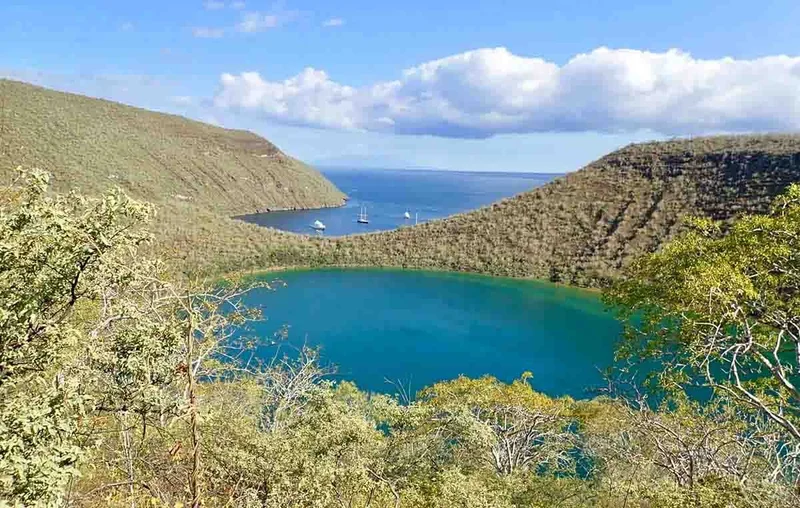
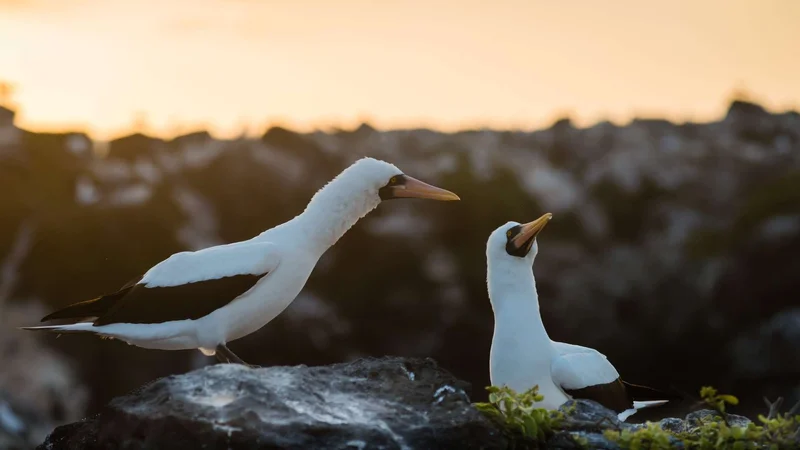
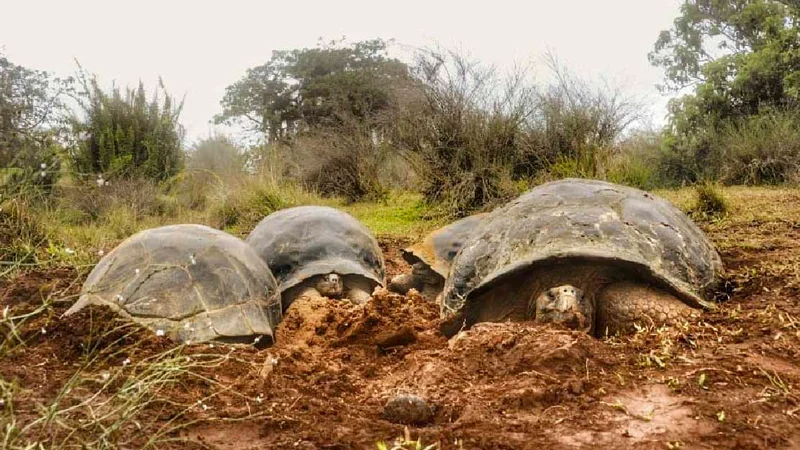
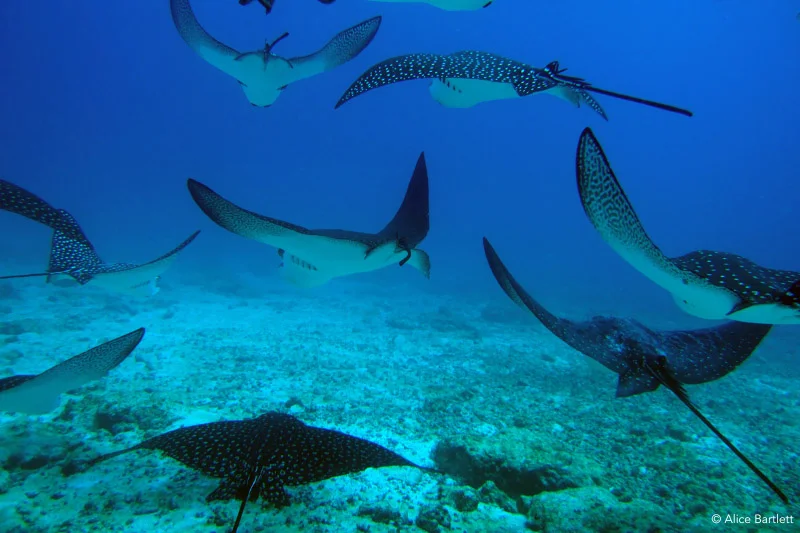















6 Day Galapagos Itinerary Includes
- Scheduled visits and activities with a professional bilingual guide
- All meals on board, snacks, purified water, tea and coffee
- Accommodation in standard cabin / suite (with balcony where applicable) with private bathroom and air conditioning
- Snorkeling equipment (mask, lenses, fins), sea-kayaks, wet-suits (some boats)
- Assistance at the Airport and 24/7 during the trip
6 Day Galapagos Itinerary Does not Include
- Air tickets to / from Galapagos from / to Quito, Guayaquil or combined route
- Entrance to the Galapagos National Park US $ 200 p.p. (cash in the Islands)
- Galapagos Control Card US $ 20 p.p. (at the airport before check-in)
- Soft and alcoholic drinks on board; personal expenses, extras and tips guide and crew (cash)
- Travel insurance with medical, cancellation and other unforeseen coverage
- Other services in Continental Ecuador and not specified in the program
6 Day Galapagos Itinerary Highlights
- Enjoy the hidden bays and many islets that sprinkle the west side of Isabela with nesting boobies and mating sea turtles
- Walk on lava as you cross the an Island that has the form of a Chinese hat for the possibility to view marine iguanas and lava lizards
- Visit the cliffs on the small South Plazas island and observe thousands of sea birds fluttering in and out of their nests
- Visit the highlands of Santa Cruz island, walk through an escalesia tree forest and encounter the giant tortoise in their natural habitat
Itinerary Map
Dates & Promotions
Dates |
|---|
No data |
Reviews
Animals you might see on this itinerary:
More information about the Galapagos Islands you visit in this 6 day itinerary:
Galapagos West Islands 6 days cruise Itinerary on board Ocean Spray
Why travel with us?
Similar Itineraries



